Imagine an Earth system component, such as an ice sheet, circulation pattern or ecosystem, as a game of Jenga.
As global temperatures gradually rise, block after block is removed from the base of the tower and placed on top. The tower becomes more and more unstable, until at some point, it can no longer support itself and it topples over.
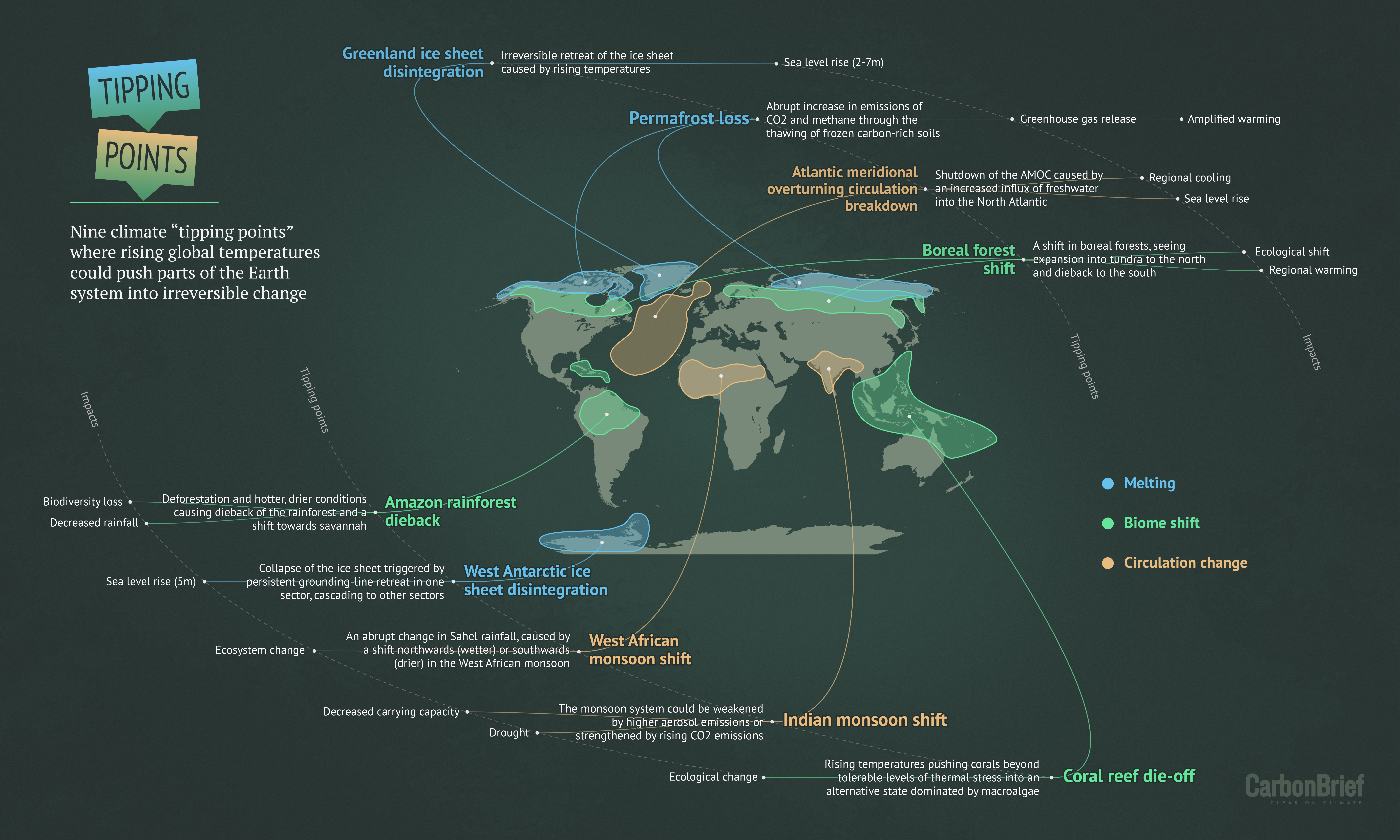
These are the mechanics behind climate tipping points . The cumulative impact of changes to the Earth system can push the system over a tipping point — a point after which serious and irreversible changes are inevitable.
GEODE lead Scott Goetz reflects on one of nine potential climate tipping points in a new article by Carbon Brief.
“An example of a tipping point in boreal forests is a situation where an extreme fire event or repeated severe events render the system incapable of regenerating as a forest ecosystem and instead shifts the system to a sparsely wooded or grassland ecosystem.”
Read more about boreal forest shift, and the other 8 tipping points, here.